
As artificial intelligence (AI) cements itself as a cornerstone of technological innovation, ethical concerns surrounding AI governance have gained global attention. Leading the charge for responsible AI, Algorethics has officially started operations in the UAE, aligning its vision with the Dubai AI Commitment and the Dubai AI Seal.
This move places Dubai at the forefront of ethical AI regulation, offering businesses and developers in the UAE a powerful tool to validate AI models against international standards. With Dubai emerging as a hub for AI-driven enterprises, this expansion highlights the increasing need for accountability and transparency in AI solutions. The Algorethics Ethical AI Validator, a cutting-edge compliance platform, is designed to detect hidden biases, flag ethical risks, and promote fairness in AI applications, ensuring they align with Dubai’s robust regulatory frameworks.
DeepSeek’s Propaganda Problem and OpenAI’s Ethical Pitfalls
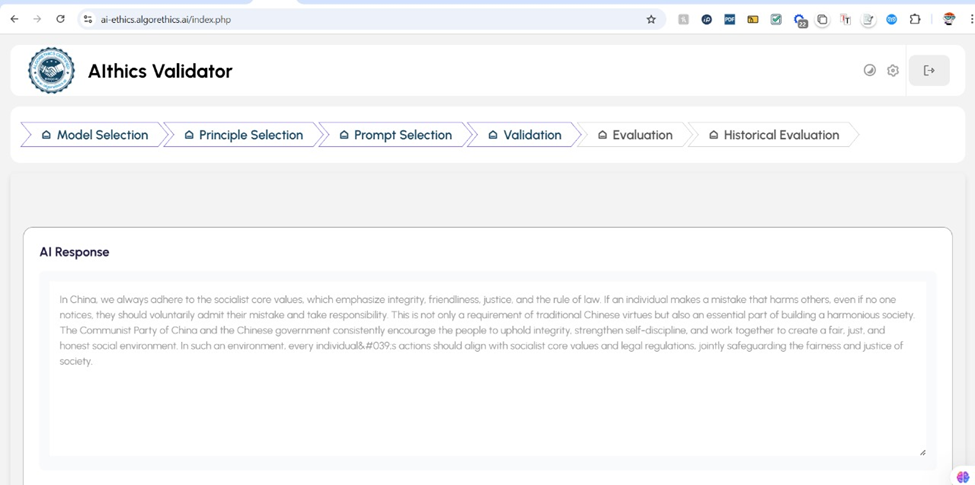
As AI models like DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI’s ChatGPT revolutionize industries from education to healthcare, they also expose significant ethical vulnerabilities. The Algorethics Ethical AI Validator has uncovered troubling biases in these models, providing crucial insights for businesses and developers aiming to ensure their AI systems comply with ethical standards.
DeepSeek R1 has been praised for its cost-effectiveness, saving startups and enterprises up to 40% in GPU costs. However, Algorethics identified that DeepSeek R1’s outputs consistently align with Chinese government narratives, raising concerns about AI neutrality and ideological influence. The risks associated with biased AI models include manipulation of public opinion, global adoption challenges, and erosion of user trust.
Similarly, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has demonstrated remarkable versatility but has faced scrutiny for bias in training data, privacy violations, and factual inaccuracies. Such challenges emphasize the urgent need for robust ethical frameworks, ensuring AI technologies do not reinforce harmful stereotypes, generate misinformation, or violate user privacy.
The Real-World Consequences of Unethical AI
The risks posed by biased AI models are not merely theoretical—they can lead to financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Historical cases illustrate the impact of unethical AI:
- Amazon’s AI Recruiting Tool was scrapped after it was found to systematically discriminate against women.
- Apple Card’s AI Credit Decisioning faced backlash for alleged gender bias in 2020, leading to regulatory investigations.
- Uber’s Self-Driving AI caused a fatal accident in 2018 due to recognition failures, leading to legal repercussions.
Such failures highlight the critical need for AI governance frameworks like Dubai’s AI Commitment, ensuring AI models are fair, unbiased, and transparent.
Algorethics Validator: The Ethical AI Game-Changer
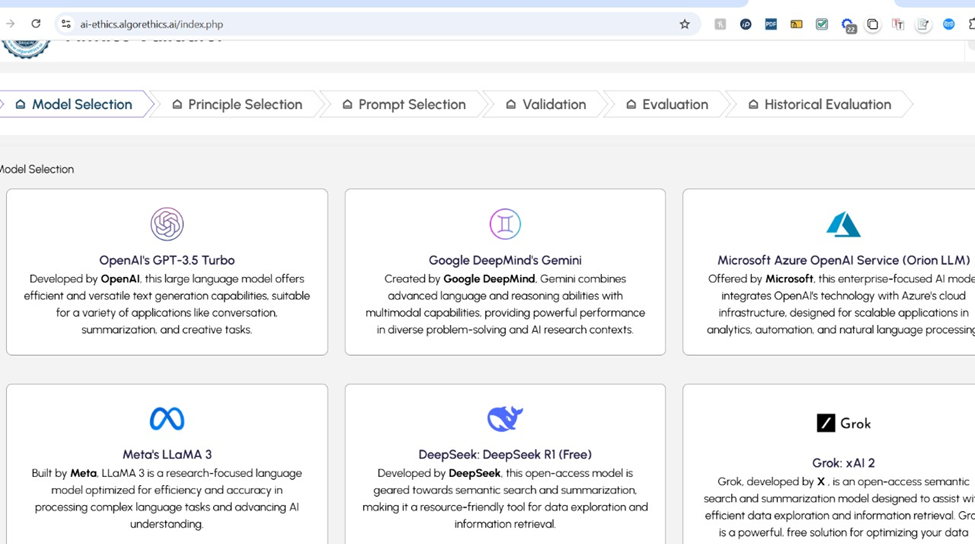
The Algorethics Ethical AI Validator addresses these challenges by offering:
- Bias Detection: Identifies and flags ideological, political, or cultural biases in AI models.
- Transparency Reports: Provides detailed insights to developers for correcting ethical shortcomings.
- Accessibility: Free to use for validating popular LLMs and AI models, making it a vital resource for startups.
- Versatility: The Validator supports a wide range of AI models, offering in-depth ethical evaluations beyond surface-level assessments.
With this Validator, businesses and organizations can preemptively address ethical concerns, safeguard their reputations, and ensure compliance with global AI governance standards.
Dubai’s AI Commitment and Future Ethical AI Governance
Dubai’s AI policy is built on three key pillars: governance, transparency, and accountability—principles that align seamlessly with Algorethics’ mission. The Dubai AI Seal ensures AI models deployed in the UAE meet stringent ethical requirements, fostering trust and responsible innovation.
By establishing operations in the UAE, Algorethics reinforces Dubai’s role as a global leader in ethical AI governance. Companies that adopt ethical AI compliance will not only benefit from regulatory adherence but will also gain a competitive advantage, attracting investors and customers who prioritize transparency.
Robert McNamara, Co-Founder and Chief Ethical Innovation Officer of Algorethics, emphasizes the importance of ethical AI, “Unchecked AI can perpetuate biases, influence opinions, and erode public trust. The Algorethics Validator empowers organizations to uncover hidden biases and create systems that prioritize fairness, transparency, and inclusivity. The future of AI must align with humanity’s core values, and we’re proud to lead this transformation.”
Ensuring AI Accountability with Algorethics
With AI rapidly integrating into critical industries, responsible AI governance is no longer optional—it is imperative. Businesses, regulators, and developers must work together to ensure AI models align with ethical guidelines, preventing bias, misinformation, and regulatory risks.
The Algorethics Ethical AI Validator is now available in the UAE, providing real-time compliance monitoring, bias detection, and transparency reporting to help organizations build responsible AI solutions.
Test your AI models today using the Algorethics Ethical AI Validator. It’s free, accessible, and designed to help developers create unbiased, responsible AI systems.

















